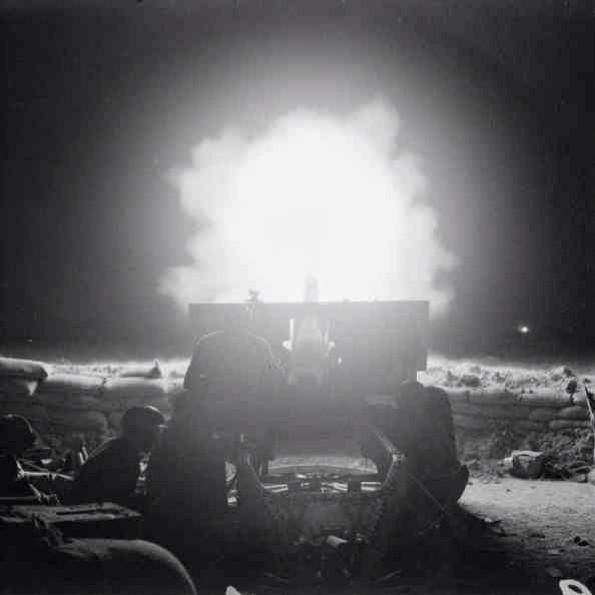
[Not a field report, but included in Kyushu Diary, Tuttle gave readers an overview of the American battle plan.]
The primary focus of operations at the end of 1945 was to get as many troops as available onto Kyushu before winter set in. The troops available would be all the Army divisions MacArthur had used in the Philippines, and whichever Marine corps divisions were not heavily involved on Okinawa, the most recent operation.
Four multi-division army corps were set up, under a general command called the Sixth Army under General Walter Krueger. Planning staffs had labeled over 30 possible landing beaches on the southern third of Kyushu, naming them in alphabetical order from east to west by automobile brands. The final plan had us using eight of them in three clusters for the X-day assault.
The Marine Corps sent its 2nd, 3rd, and 5th divisions as the Fifth Amphibious Corps. They would land on the west coast, south of the city of Sendai. The First Corps, Army divisions 25th, 33rd, and 41st, would land on the east coast, either side of the city of Miyazaki.
South of that in Ariake Bay the 1st Cavalry Division, 43rd Infantry Division, and the Americal Division would land as the Eleventh Corps. Another corps, the Ninth, on X-2 has already made an elaborate fake landing operation toward Shikoku far to the northeast. Its 77th, 81st, and 98th infantry divisions can land as needed later. They are penciled in for a landing south of the Marines on X+3 or X+4. Ninth Corps also had the 112th “Regimental Combat Team” , which could deploy independently. Incidentally, the 98th is an all new unit, the only one here with no combat experience.
Ahead of the multiple corps, the 40th Infantry Division, reinforced with the 158th Regimental Combat Team, started landing on the smaller islands south and west of Kyushu, to eliminate them as threats to the main fleet once it arrived.
What we need out of Kyushu most of all is airbases. You may have noticed, B-29 bombers are not small. They need room to stretch out those long wings, and they prefer wide long runways. In addition, there are supply depots and workshops and barracks for a million men (or more) to build. But Kyushu does not have an abundance of flat land to offer. It is woven from a coarse thread of steep ridges and volcanic peaks, interrupted only briefly by flat valleys and a few small plains. To get enough space for our uses, and secure it from Japanese long range artillery or sneak attack, we plan to push well into the hills north of the last set of valleys.
As a layman looking at all this, the invasion plan at first looked like a focused application of awesome force, and it was impossible to see how such a large and well equipped invader could be turned away. But I had been at this a little while by then, and I did a little calculating. I’m sure real staff officers in many headquarters and Pentagon offices had run the same numbers many times.
Okinawa is about 5 miles across in its southern portion where we had four divisions abreast fighting stiff resistance for two months to advance about 15 miles, taking casualties all the way. Southern Kyushu is 90 miles wide, and we plan to land maybe 13 divisions. That would spread forces out almost six times as thin. Total area to be taken is well over 5,000 square miles. They talk about having ‘maneuver room’ and ‘flexible force concentration’ to overcome this. Time will tell.